Diploma Programme (DP)
Career-related Programme (CP)
What is the Diploma Programme (DP)?
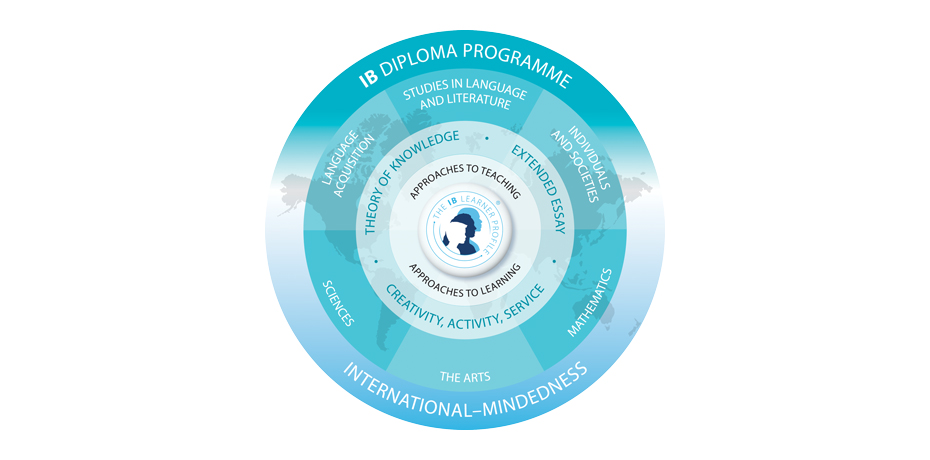
The Diploma Programme (DP) is for those aged from 16 to 19 and allows students to obtain an internationally recognized university-entrance qualification (The IB Diploma) when they complete the prescribed curriculum for two years and achieve certain grades after passing the final examination. The programme is conducted in English, French, or Spanish, except for the subjects that are subject to the DP in Japanese.
1 Curriculum of the Diploma Programme (DP)
The DP curriculum consists of the following six groups (subjects) and three compulsory requirements called the “Core.”
Students choose one subject each from six groups, and study those six subjects for two years. However, subjects in Arts (Group 6) can be replaced with subjects in other groups.
In addition, from the perspective of preparing the knowledge and skills in a specialty that will be required at university and for their future occupations, students will study three to four out of the six subjects as the
-
Group 1
Language and Literature (mother tongue)
Subjects:
Language A: Literature
Language A: Language and Literature
Language A: Literature and Drama (for the SL only)(*). -
Group 2
Language Acquisition (foreign language)
Subjects:
Language B
Classical Language
Beginner Language (for the SL only). -
Group 3
Individuals and Societies
Subjects:
Geography, History, Economics, Business and Management, Information Technology and Global Society, Philosophy, Digital Society, Psychology, Social and Cultural Anthropology, Global Politics, World Religions (for the SL only), and Environmental System and Society(*). -
Group 4
Science
Subjects:
Biology, Chemistry, Physics, Computer Science, Design Technology, Sports, Exercise and Health Science, and Environmental System and Society(*). -
Group 5
Mathematics
Subjects:
Maths – Analysis and Approaches
Maths – Applications and Interpretations. -
Group 6
Arts
Subjects:
Music, Fine Arts, Dance, Film, Drama, and Literature and Drama (for the SL only)(*).
(*) “Literature and Drama” is a cross-curricular subject for Groups 1 and 6. “Environmental System and Society” is a cross-curricular subject for Groups 3 and 4. Students can register for these subjects in either group.
In addition to the above six groups, three subjects of “Theory of Knowledge (TOK),” “Extended Essay (EE),” and “Creativity, Activity, Service (CAS)” are designated as compulsory core subjects. The existence of these three core subjects can be seen as a major characteristic of IB education, emphasizing inquiry-based learning and whole-person education. However, since there may be no comparable subjects in Japan, details about these subjects are further explained below.
-
Extended Essay (EE)
Students undertake individual research in the field they are interested in and finish with a 4,000-word paper (8,000 characters in Japanese).
-
Theory of Knowledge (TOK)
A subject in which students learn what the essence of knowledge is. IB advocates constructivism, stating that “knowledge is always constructed by people.” Students explore frameworks that our predecessors used to understand the world, learn how to pose meaningful questions that are useful in real life and cut to the essence of things without falling into binary oppositions, and how to engage with these questions.
-
Creativity, Activity, Service (CAS)
Students engage in experiential learning through artistic activities that involve creative thinking, physical activities, and unpaid voluntary exchange activities.
2 DP Assessment
To obtain the IB qualification, students must complete the entire DP curriculum and, in principle, gain at least 24 out of 45 points through external assessment, such as the IB Examinations, and internal assessment.
Seven points are given to each of six subjects (which makes 42 points in total). In addition, as to the Core, compulsory requirements, a maximum of 3 points will be awarded according to the combination of assessment results of the TOK and EE. (The CAS is not applicable for assessment.)
The IB Examinations are held twice a year around the world at once to accommodate the academic year in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. In the case of Article-one schools in Japan, the IB Examinations are held in November of the third year, and the final score is reported on January 5 of the following year. Sample exam papers for the IB Examinations can be viewed at the links below.
- Sample Exam Papers (English version)
- Sample Exam Papers (Japanese version): To view, registration for Consortium membership is required. Consortium Membership Registration
3 DP in Japanese (Dual Language Diploma Programme: DLDP)
In principle, DP classes and examinations must be carried out in English, French, or Spanish. However, currently, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and the IB cooperate to develop a programme that enables schools to provide some DP subjects in Japanese, too.
Subjects and others that are subject to the DP in Japanese
Subjects that can be or are scheduled to be implemented in Japanese are as follows:
- Subjects in detail:
Language A: Literature and Language A: Language and Literature among Group 1 (Language and Literature)
Geography, History, and Economy among Group 3 (Individuals and Societies)
Biology, Chemistry, and Physics among Group 4 (Science)
Maths – Analysis and Approaches and Maths – Applications and Interpretations among Group 5 (Mathematics)
Music and Fine Arts among Group 6 (Arts)
*Even in the DP in Japanese, it is required for students to complete two out of six subjects (usually, one more subject in addition to Group 2 (Foreign Language)) in English or other languages. - All of the Core, three compulsory requirements:
Theory of Knowledge (TOK), Extended Essay (EE), and Creativity, Activity, Service (CAS)
*As for the subjects that can be conducted in Japanese, subject guidebooks and others that are translated into Japanese can be viewed at the following links. (All of the documents subject to translation are not listed on the site since some subject guidebooks are currently being translated. Such non listed documents will be posted as soon as the translation is completed.)
What is the Career-related Programme (CP)?
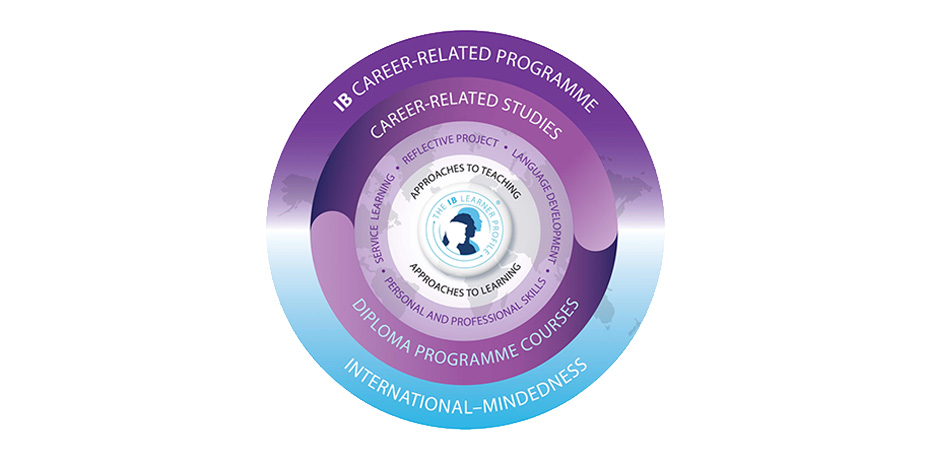
The Career-related Programme (CP) is for those aged 16 to 19 and is related to career and vocational education. It emphasizes the acquisition of skills necessary for lifelong career development. (Newly established in 2012) Some of the subjects (such as a project of “Reflecting”) are conducted in English, French, or Spanish.
The CP curriculum provides a framework so that schools can flexibly respond to the career and vocational education that each school offers.
The CP is composed of the following three frameworks:
1 Some of the subjects in the Diploma Programme (DP)
In the CP, students must take at least two of the subjects from the DP (among Group 1 to Group 6). (Students can freely select and combine subjects from both levels, Higher Level and Standard Level.) They can even select subjects applicable to the DP in Japanese.
2 The Core
- Approaches to learning:
Learning, focusing on critical and ethical thinking, cross-cultural understanding, and communication skills. More than 90 hours of study. - Community and service:
Engaged in community service outside of the classroom. Approximately 50 hours of study. - Language Development:
Studying foreign language for at least 50 hours. - The reflective project:
Examining specific issues related to career education from an ethical perspective, being engaged in approximately 40 hours of individual research both inside and outside of the classroom, and thus developing research and communication skills.
3 Career-related learning
The CP is a programme developed to support and supplement the career-related education provided by each school, and career and vocational education is provided by each school.
The curriculum for each subject of the DP, different from the PYP and MYP, is provided by the IB. If you would like to deepen your understanding of the DP, please read the overview and the guidebook by subject, which is posted in the “Resources for Schools in Japan” on the official IB website.
